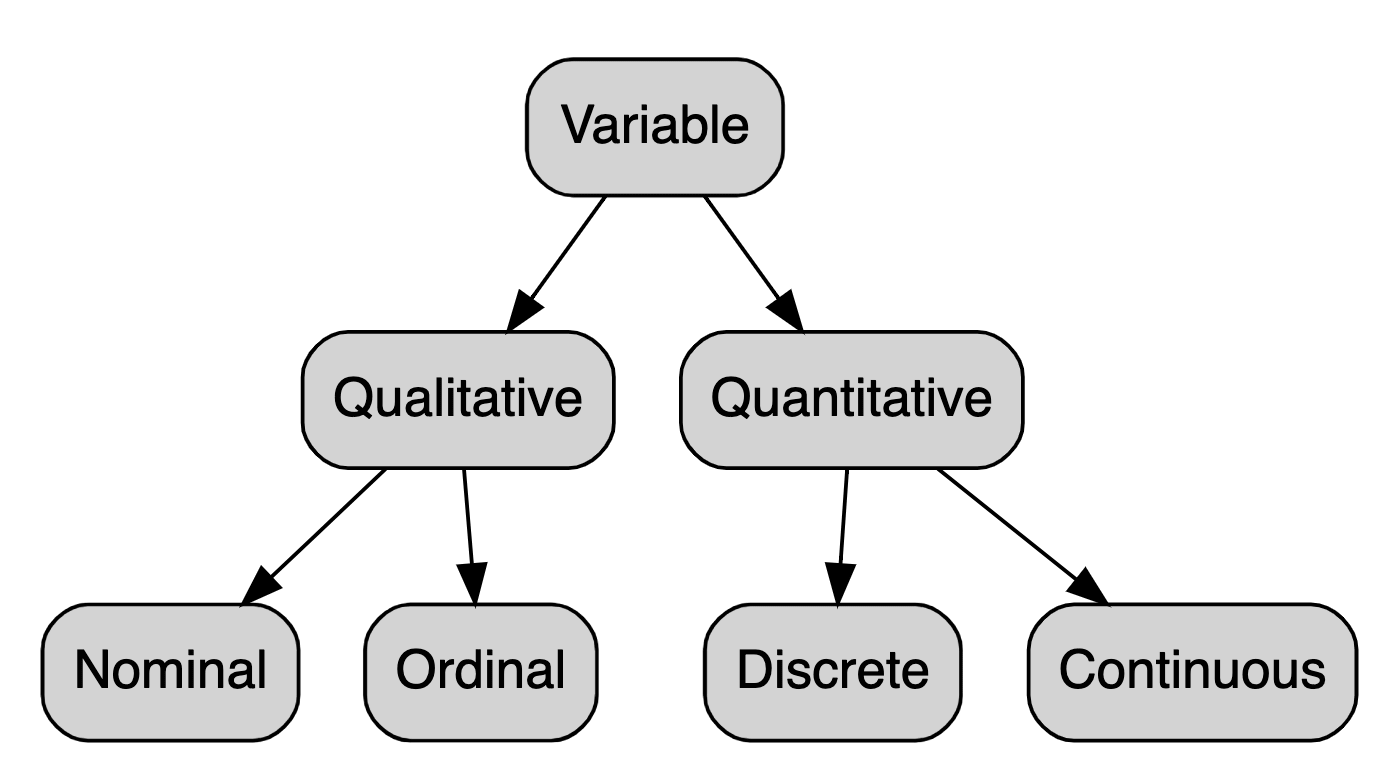
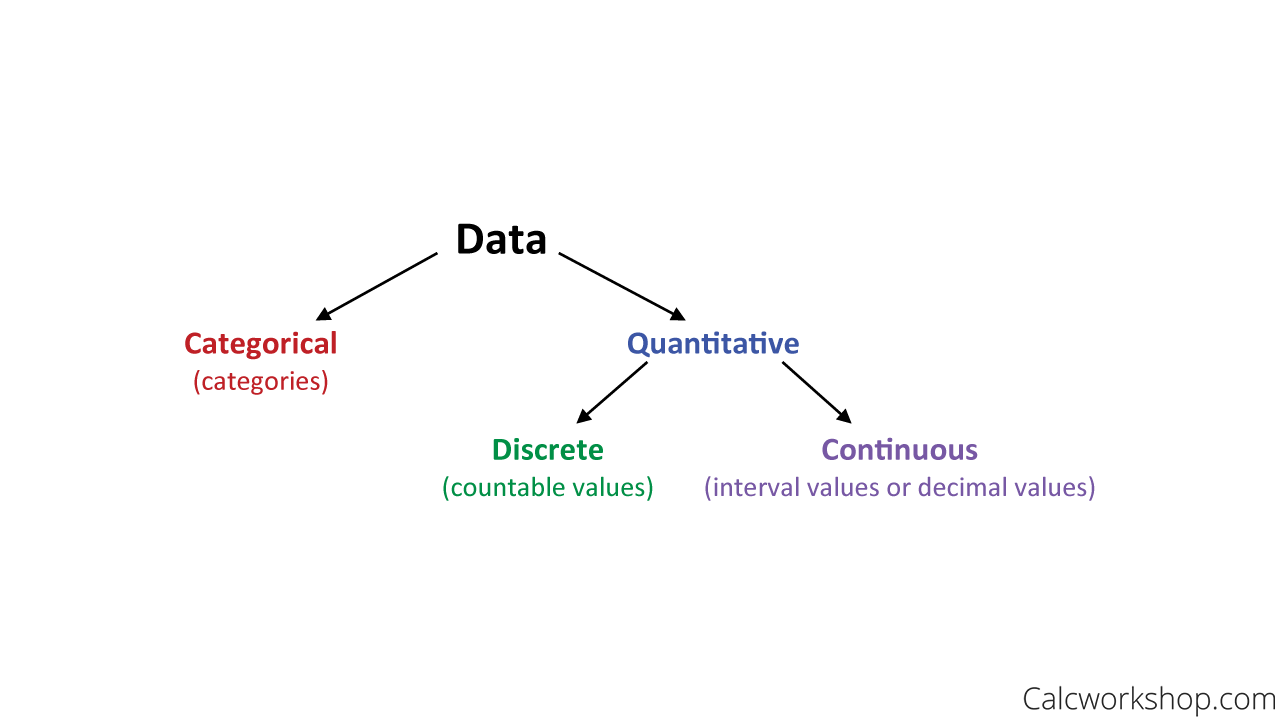
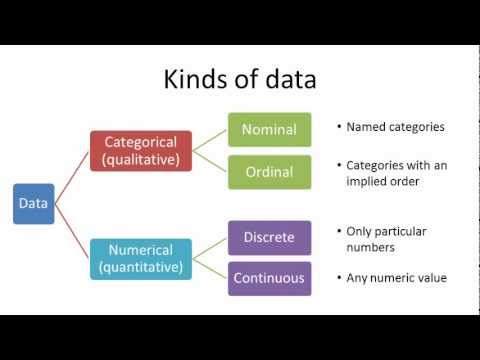
Quantitative variables have numerical values with. Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups.
 Variable Types And Examples Stats And R
Variable Types And Examples Stats And R
Box plots of continuous variable values for each category of categorical variable.
Quantitative and categorical variables. We have already discussed methods for analysis of data with a quantitative outcome and categorical explanatory variables ANOVA and ANCOVA. Categorical variable Categorical variables contain a finite number of categories or distinct groups. Variables that take on names or labels.
For example a binary variable such as yesno question is a categorical variable having two categories. This includes rankings eg. Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts eg.
Categorical data might not have a logical order. One categorical variable and other continuous variable. A quantitative variable can be measured and has a specific numeric value.
Also indicate the level of measurement for the variable. Egorical outcome and a single categorical explanatory variable. Categorical variables are those that provide groupings that may have no logical order or a logical order with inconsistent differences between groups eg the difference between 1st place and 2 second place in a race is not equivalent to the difference between 3rd place and 4th place.
Hover your mouse over the test name in the Test column to see its description. Variables can be classified as categorical or quantitative. In our medical example age is an.
Sometimes referred to as numeric variables these are variables that represent a measurable quantity. In this case height is a quantitate variable while biological sex is a categorical variable. Examples of quantitative variables include height weight age salary temperature etc.
Finishing places in a race classifications eg. Quantitative data belong to ordinal interval or ratio classes of measurements. Quantitative variables can be classified as discrete or continuous.
In statistics variables can be classified as either categorical or quantitative. Any variables that are not quantitative are qualitative or a categorical variable. Height weight or age.
Quantitative variables take numerical values and represent some kind of measurement. Quantitative data are information that has a sensible meaning when referring to its magnitude. Categorical data belong to the nominal.
The How To columns contain links with examples on how to run these tests in SPSS Stata SAS R and MATLAB. This includes rankings eg. For example we may want to compare the heights of males and females.
A categorical variable sometimes called a nominal variable is one that has two or more categories but there is no intrinsic ordering to the categories. Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts eg. Graphs with groups can be used to compare the distributions of heights in these two groups.
The Methodology column contains links to resources with more information about the test. Side-by-side dot plots means measure of uncertainty SE or confidence interval Do not link means across categories. The methods in this section are also useful for observational data with two categorical outcomes and no explana-tory variable.
Characteristics of Categorical and Quantitative data. Height weight or age. For each of the variables described below indicate whether it is a quantitative or a categorical qualitative variable.
For example categorical predictors include gender material type and payment method. Categorical variables take category or label values and place an individual into one of several groups. Categorical data are often information that takes values from a given set of categories or groups.
This table is designed to help you choose an appropriate statistical test for data with one dependent variable. Finishing places in a race classifications eg. Correlation is often used for describe a relationship between two quantitative variables quantitative quantitative while relationship and association are used for two categorical variables categorical categorical or for a categorical - quantitative relationship study categorcial quantitative.
Sometimes referred to as categorical variables these are variables that take on names or labels and can fit into categories. Often times we want to compare groups in terms of a quantitative variable. Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups.
 Introduction And Types Of Data Flashcards Quizlet
Introduction And Types Of Data Flashcards Quizlet
 Everything About Data Science Types Of Statistical Data Numerical Categorical And Ordinal
Everything About Data Science Types Of Statistical Data Numerical Categorical And Ordinal
 Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Card Sort Activity Math Love
Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Card Sort Activity Math Love
 Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Ppt Download
Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Ppt Download
 What Is Categorical Data Defined W 11 Examples
What Is Categorical Data Defined W 11 Examples
 Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Definition Examples
Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Definition Examples
 Data Continuous Vs Categorical
Data Continuous Vs Categorical
 Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Youtube
Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Youtube
 Types Of Variables Definitions And Easy Examples
Types Of Variables Definitions And Easy Examples
 Ppt Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5649052
Ppt Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5649052
 Data Statistics 2 Data Can Be Numbers Record
Data Statistics 2 Data Can Be Numbers Record
 Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Youtube
Categorical Vs Quantitative Variables Youtube

 Categorical Vs Quantitative Data Statistics For The Social Sciences
Categorical Vs Quantitative Data Statistics For The Social Sciences
 Quantitative Categorical Variable Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Quantitative Categorical Variable Page 1 Line 17qq Com
 What Is Discrete Categorical Ordinal Numerical Non Numerical And Continuous Data Socratic
What Is Discrete Categorical Ordinal Numerical Non Numerical And Continuous Data Socratic
 Transform A Code Into A Categorical Document Variable Maxqda
Transform A Code Into A Categorical Document Variable Maxqda
 Categorical Vs Quantitative Data Concepts In Statistics
Categorical Vs Quantitative Data Concepts In Statistics
 Thresholds Adopted To Convert Quantitative Into Categorical Variables Download Table
Thresholds Adopted To Convert Quantitative Into Categorical Variables Download Table
Cari Blog Ini
Label
- 1800s
- 1820s
- 18th
- 1920s
- 50th
- about
- absence
- absent
- absolute
- abstract
- academic
- academy
- accelerated
- accent
- accents
- accept
- acceptance
- access
- account
- accounting
- accreditation
- accredited
- acronym
- acting
- active
- activities
- adaptation
- address
- addressing
- administration
- admission
- admissions
- adulta
- adults
- advantage
- advantages
- adverb
- adversity
- affairs
- affect
- africa
- after
- agencies
- agency
- agent
- agents
- airforce
- alarm
- alexander
- algebra
- allowed
- alpha
- alphabet
- amber
- america
- american
- americans
- analysis
- analyze
- anatomy
- ancient
- anglo
- animal
- anthropology
- anyone
- anything
- apartment
- apostles
- appalachian
- applicants
- application
- applied
- apply
- applying
- aptitude
- arabic
- architects
- area
- argument
- argumentative
- aristotle
- army
- arrive
- arrows
- article
- artifact
- artifacts
- artistry
- arts
- aruba
- assessment
- assessments
- assimilation
- assistant
- associate
- associates
- asterix
- asvab
- athletic
- attacked
- attend
- attention
- attila
- autobiographical
- autobiography
- average
- aztec
- bachelor
- bachelors
- back
- bags
- bald
- balls
- bank
- banking
- based
- beads
- beautiful
- because
- become
- becoming
- beginner
- beginners
- behavior
- behaviorism
- behaviors
- being
- beliefs
- bella
- below
- benchmark
- benefits
- best
- better
- between
- bible
- biochemistry
- biologists
- biology
- black
- blackbeard
- blend
- blends
- bloom
- boarding
- boats
- book
- boys
- brain
- breaker
- breakers
- breaking
- breaks
- broadcasting
- broker
- bronx
- bulb
- burlap
- business
- bypass
- caddos
- calculate
- calculating
- calculator
- calculus
- call
- called
- cameras
- campaign
- campbell
- canada
- candle
- candles
- capitalize
- card
- cardinal
- cardiologist
- cards
- care
- career
- caribbean
- catapult
- catapults
- catcher
- categorical
- cbest
- center
- central
- ceremony
- certificate
- certification
- challenges
- change
- changes
- changing
- character
- characteristics
- characters
- charlotte
- cheat
- check
- cheerleaders
- cheerleading
- chemical
- chemistry
- cherokee
- child
- choctaw
- choices
- choose
- chose
- christ
- christmas
- churches
- ciao
- city
- civilization
- claims
- class
- classes
- classroom
- clause
- clean
- cleanse
- closing
- clothes
- clothing
- coaches
- coalinga
- coast
- cogat
- college
- colleges
- colonies
- colony
- color
- colors
- comma
- commercial
- common
- communication
- communicator
- community
- competent
- completed
- components
- comprehension
- computer
- concept
- conclude
- concluding
- conclusion
- conclusions
- concrete
- conflicts
- conjugation
- cons
- consonant
- constructivism
- constructivist
- content
- contextual
- contract
- contrast
- contributions
- convert
- cooked
- cooking
- cool
- copy
- core
- cosmetology
- cost
- could
- council
- count
- countries
- course
- courses
- cover
- create
- created
- creating
- creative
- credibility
- credits
- criminal
- criterion
- critical
- critique
- cross
- cultural
- culture
- cultures
- cuny
- currency
- currently
- curriculum
- cursive
- curve
- curves
- custom
- customs
- cute
- cutting
- cypress
- dabate
- dallas
- damaging
- dance
- dangling
- data
- date
- dates
- deactivate
- deans
- debates
- decisions
- declaration
- decline
- decoding
- defensive
- definition
- definitions
- degree
- degrees
- delta
- democrats
- denny
- dependent
- dependents
- dermatologist
- descriptive
- deserve
- design
- designing
- development
- device
- devices
- diagnostic
- dialogue
- dialysis
- dibels
- diction
- difference
- differences
- different
- diploma
- directional
- director
- disabled
- disadvantages
- disciples
- discuss
- discussion
- divison
- doctor
- doctorate
- does
- donate
- donation
- donna
- dont
- dorm
- dorms
- double
- download
- dramatic
- draw
- drawing
- dream
- drop
- dual
- eagle
- earn
- easiest
- ecological
- ecology
- education
- effect
- egypt
- egyptian
- egyptians
- election
- elections
- electrical
- elementary
- elizabethan
- elongate
- emergency
- emory
- employees
- encoding
- ending
- engine
- engineer
- engineerig
- engineering
- england
- english
- enhanced
- entrance
- envelope
- enviorment
- environmental
- erase
- essay
- essays
- estate
- ethical
- ethics
- european
- evaluate
- events
- exactly
- exam
- example
- examples
- excel
- except
- expelled
- expenses
- experiment
- expository
- expulsion
- facs
- fact
- facts
- fafsa
- fail
- failed
- fair
- fake
- fall
- family
- farm
- fashion
- fasion
- faster
- features
- federal
- feudalism
- field
- files
- fill
- film
- final
- financial
- find
- fine
- finish
- finishing
- fire
- firenze
- first
- flag
- flakes
- flashlight
- fleur
- florida
- food
- foods
- football
- foreign
- forensic
- format
- forms
- foster
- founded
- four
- fourth
- framework
- free
- french
- freshman
- freshmen
- friendly
- friends
- from
- full
- function
- fund
- funded
- funny
- gaelic
- game
- games
- geds
- general
- genghis
- genres
- geography
- georgia
- german
- germany
- gesell
- getting
- give
- glasses
- globalization
- glue
- gmail
- goals
- gold
- good
- goodbye
- goodnight
- government
- gown
- gpas
- grabbers
- grade
- graders
- grades
- grading
- graduate
- graduates
- graduating
- graduation
- grammar
- grandchildren
- grant
- grants
- greece
- greek
- group
- growth
- guide
- guides
- guitar
- gulf
- gunsmithing
- gwam
- hair
- hand
- handed
- hands
- happens
- happy
- hard
- harvard
- have
- having
- hbcu
- head
- heading
- hebrew
- hellen
- hellenistic
- hello
- hemodialysis
- high
- higher
- highschool
- hills
- historically
- history
- hobbes
- home
- homecoming
- homes
- homeschool
- honor
- honorary
- honors
- hopkins
- hospital
- hospitality
- hours
- house
- housing
- however
- human
- humane
- humanitoes
- humans
- hvac
- icebreaker
- icebreakers
- idea
- idealism
- ideals
- ideas
- identify
- identifying
- immigrants
- impact
- impacts
- impeach
- imperialism
- importance
- important
- improve
- inaugural
- included
- income
- independence
- india
- indian
- indoor
- induction
- industrial
- influence
- Information
- initiation
- instead
- institute
- interactive
- interesting
- intergrated
- internship
- interpersonal
- intership
- interview
- into
- introduction
- introductions
- invented
- invention
- inventions
- invitation
- involve
- iranians
- ireland
- irish
- iroquois
- italian
- items
- jeffersonian
- jeopardy
- jersey
- jesuit
- jesus
- jobs
- join
- joining
- junior
- juniors
- justice
- kaplan
- kappa
- katana
- kaufman
- keller
- khan
- kids
- kill
- kind
- kindergarten
- know
- known
- labor
- lady
- language
- languages
- large
- last
- late
- latin
- lawyer
- league
- learn
- learned
- learning
- length
- lesson
- lessons
- letter
- letters
- level
- levels
- liberal
- license
- licensed
- life
- lifestyle
- light
- like
- limit
- list
- listening
- lists
- literacy
- literal
- literature
- little
- living
- loan
- loans
- local
- locker
- login
- long
- longer
- longitude
- look
- lords
- love
- luck
- macroeconomic
- made
- main
- mainstreaming
- major
- majors
- make
- makes
- making
- males
- manage
- management
- many
- marine
- marketing
- mascot
- maslow
- maslows
- master
- masters
- mates
- math
- matter
- mayor
- mcat
- mean
- meaning
- means
- media
- medical
- medicine
- medium
- memorize
- memory
- meps
- mesopotamian
- methods
- mexico
- middle
- migrant
- military
- mini
- minimum
- minor
- minute
- miss
- mitchell
- mnemonic
- mockingbird
- modeling
- models
- modern
- modernism
- modernist
- money
- monitor
- monitoring
- morning
- mortar
- most
- movie
- moving
- much
- multicultural
- multiple
- music
- musical
- name
- names
- national
- native
- nature
- navy
- nclex
- near
- need
- needed
- needs
- negative
- negro
- nelson
- neonatal
- netflix
- newspaper
- nkjv
- nominative
- norm
- nostalgic
- notification
- noun
- nouns
- nova
- number
- numbered
- nurse
- nurses
- nursing
- nusing
- obgyn
- object
- objective
- objects
- obtain
- occupational
- oceanographer
- offer
- ohio
- oneself
- online
- open
- opening
- operations
- optometry
- order
- outfitters
- outline
- overall
- overcoming
- overthrow
- pacer
- page
- paper
- papers
- paragraph
- part
- partial
- participle
- parts
- pass
- passing
- passive
- patients
- patterns
- paul
- pell
- penn
- people
- percent
- percentages
- percentile
- performance
- performing
- period
- persian
- personal
- perspective
- persuasive
- pharmacology
- pharmacy
- phoenix
- phonics
- photochemical
- photographic
- photography
- photos
- phrase
- physical
- physician
- physiology
- pictures
- pilot
- placement
- plan
- plant
- plasma
- plastic
- plato
- play
- plays
- pledge
- pledging
- plot
- plural
- poem
- poetry
- point
- pointillism
- pole
- polish
- popcorn
- popular
- population
- portfolio
- positive
- possessive
- post
- postcard
- practice
- predicate
- predicated
- preoperational
- prep
- prepare
- prepositional
- preschool
- preschoolers
- prescriptive
- presentation
- press
- pressure
- preterite
- prima
- primary
- printable
- printing
- priority
- private
- probability
- production
- products
- professor
- program
- programs
- progress
- project
- projects
- prom
- pronoun
- pronounce
- pronouns
- proofreading
- proportion
- pros
- protective
- psychology
- public
- puerto
- purpose
- puzzle
- quantitative
- quarter
- question
- questions
- quickly
- quintile
- quoting
- radiologist
- radiology
- raise
- raising
- range
- ratio
- reached
- reading
- realism
- reasons
- rebus
- recognition
- recognize
- recommendation
- referenced
- reflection
- reflective
- reflexive
- refuge
- regents
- regional
- regions
- register
- reinforcement
- reinforcer
- release
- reliability
- relic
- religion
- remember
- remove
- removing
- rent
- repair
- repay
- repeating
- replace
- report
- reports
- require
- required
- requirement
- requirements
- research
- residents
- respected
- respiratory
- results
- resume
- retake
- reunion
- reunions
- review
- revolution
- rhetorical
- rhit
- rica
- ride
- rituals
- rock
- role
- roles
- room
- root
- rotc
- rubric
- rules
- rush
- salaries
- sale
- same
- sample
- samples
- samurai
- sang
- sanskrit
- satire
- saxon
- scantron
- scared
- scene
- schol
- scholarship
- scholarships
- school
- schooling
- schools
- science
- score
- scores
- scoring
- scotland
- scottish
- seals
- second
- secondary
- section
- sectional
- security
- self
- sell
- sells
- send
- senior
- seniors
- sentence
- sequence
- sequential
- service
- setting
- setup
- sewn
- sheet
- shoe
- short
- should
- show
- siblings
- side
- sight
- sigma
- sign
- simple
- simularitys
- sized
- skill
- skills
- skip
- sleeves
- small
- smog
- social
- society
- software
- some
- someone
- someones
- song
- songs
- sorority
- sound
- sounds
- soup
- source
- spaces
- spanish
- speak
- speaker
- speakers
- speaking
- speech
- speeches
- spell
- spirit
- spoken
- sports
- square
- stages
- stamped
- stand
- standardized
- stanford
- start
- state
- statement
- statements
- states
- statistics
- stay
- steps
- sticks
- stna
- stoles
- stone
- stop
- stopped
- stories
- strategies
- strengths
- structures
- student
- students
- studies
- study
- style
- styles
- subject
- submit
- suffixes
- suite
- summarize
- summarizing
- summary
- summer
- sung
- surgeon
- survival
- suspended
- suspension
- swedish
- syllables
- symbol
- system
- systems
- table
- tables
- take
- talent
- talk
- tampa
- tassel
- tassels
- tbas
- teach
- teacher
- teachers
- teaching
- team
- teams
- technical
- technician
- technology
- teepee
- template
- tenses
- terminology
- terra
- test
- testing
- tests
- texas
- than
- thank
- that
- their
- theme
- themes
- theoretical
- theory
- there
- thesis
- things
- thought
- three
- tier
- tiers
- timberline
- time
- times
- tips
- title
- titles
- toastmasters
- today
- tone
- topics
- toys
- traditional
- training
- transcript
- transfer
- transferring
- transition
- translate
- translated
- treasurer
- trebuchet
- trenton
- trial
- tribes
- tribute
- trip
- tuition
- turning
- tutor
- tying
- type
- types
- typing
- ucla
- under
- undergraduate
- uniforms
- union
- united
- units
- universities
- university
- used
- using
- valedictorian
- validate
- validity
- value
- values
- variables
- varsity
- vassar
- verb
- verbal
- verbs
- verizon
- veteran
- veterinarian
- video
- videos
- view
- views
- viking
- villanova
- virginia
- voice
- volleyball
- vowel
- want
- warrant
- washington
- watch
- ways
- weaknesses
- weapons
- wear
- wearers
- weather
- weighted
- welfare
- were
- wesleyan
- west
- what
- whats
- wheel
- when
- where
- which
- while
- white
- whom
- widow
- wigs
- will
- window
- windows
- with
- without
- women
- wonderlic
- word
- words
- work
- workers
- works
- world
- worry
- worship
- worth
- write
- writing
- xenia
- xray
- year
- yearbooks
- years
- yellow
- york
- young
- your
