Each level of skill is associated with a verb as learning is an action. This can increase the back-and-forth dialogues teachers have.
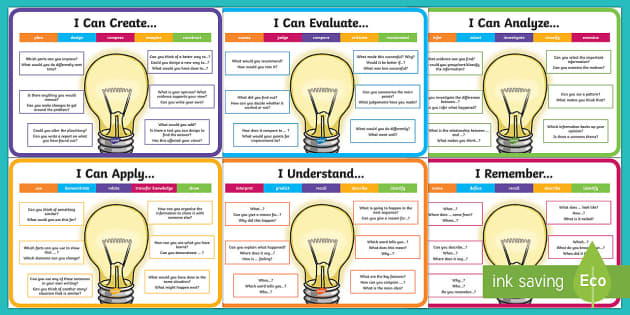 Bloom S Taxonomy Posters Using Questions For Learning Blooms
Bloom S Taxonomy Posters Using Questions For Learning Blooms
Asking children more complicated questions helps them become self-directed thinkers.

Bloom taxonomy questions for preschoolers. State in your own words. Which are the facts. Ask students to recall information.
However Blooms Taxonomy can be applied to kindergarten students in a few simple steps. 1 If you are new to the taxonomy. Using Blooms Taxonomy Questioning to Extend Preschoolers Thinking.
Children develop at different rates and may surprise you with their answers. Blooms Taxonomy for Preschoolers inspired by the Machines Project at Bellevue Discovery Level 1 Knowledge. 25 Question Stems Framed Around Blooms Taxonomy by TeachThought Staff While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself.
Blooms Taxonomy to ask preschoolers higher-level questions. Find this Pin and more on Preschool activitiesby Christine Harris-Wazinski. Can you tell why.
If you are homeschooling your child or are planning to homeschool its a system you want to become familiar with. Who was it that. Remembering understanding applying analyzing evaluating and creating.
Who spoke to. Moving Beyond Who What When Where and Why. Each category builds on the mastery of the previous one.
This resource uses Blooms Taxonomy to structure questions for reading. This includes questions like. Use it to encourage independent learning or as a prompt for children to ask each other questionsExplore more of our resources on questions for reading.
In Blooms Taxonomy there are six levels of skills ranked in order from the most basic to the most complex. Blooms Taxonomy can easily be overlooked for students in kindergarten because the students are so young. Teachers often use Benjamin Blooms taxonomy of thinking skills when planning their curriculum.
Using an adaptation of Blooms Taxonomy to think about the types of questions teachers ask children this article focuses on intentionally using questions that challenge children to analyze evaluate and create. What does this mean. Can you name the.
Normally represented in pyramid form the categories of Blooms Taxonomy are. Sample Question Stems Based on Revised Blooms Taxonomy Remember Understand Apply Who. They plan their questions to match a childs current level and encourage him to make.
Blooms Taxonomy is named after Benjamin Bloom a psychologist who in 1956 developed the classification of questioning according to six levels of higher level thinking. Using Blooms Taxonomy Questioning to Extend Preschoolers Thinking. This taxonomy ranges from lower to higher levels of cognitive thinking.
Bloom 1956 has provided us with his taxonomy to assist us to compose questions on different levels of thinking. These types of questions only require children to use memorization in order to respond. Blooms Taxonomy Sample Questions Remember Useful Verbs Sample Question Stems List Locate Name Recognize State Describe Recall Repeat Retrieve What happened after.
Who what where when and why. Find the meaning of. Can you name all the.
As a teacher you should ensure that the questions you ask both in class and on written assignments and tests are pulled from all levels of the taxonomy pyramid. After reading a few pages ask students to recall some of the information from the fairy tale that youve read this far. Remembering is the first level of Blooms Taxonomy.
Blooms Taxonomy is a hierarchy of cognitive skills that most teachers use as they plan units of study. Blooms Taxonomy includes six levels of questioning. Describe what happened at.
Require students to explain why. Understanding is the next level. These levels are I will shortly provide more detail of each level.
For example ask students to name all the characters in a fairy tale. Through ongoing observation and assessment effective teachers keep track of each childs activities and skills. Remembering understanding applying analyzing synthesizing and evaluating.
Bloom includes in his taxonomy lower-order-thinking skills. Name a machine you have at home. Which is true or false.
Blooms Taxonomy is a teaching strategy developed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom outlining a series of learning categories from remembering to creating. The revised theory lists to suit the 21st Century relevance which is about Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating and Creating. Exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Creating a solid base of content knowledge is important but preschoolers learning can be deeper and more complex. Explore some of the ways you can ask children questions throughout. What does it mean.
What is the best one.
Halaman
Sparkhouse
Cari Blog Ini
Label
- 1800s
- 1820s
- 18th
- 1920s
- 50th
- about
- absence
- absent
- absolute
- abstract
- academic
- academy
- accelerated
- accent
- accents
- accept
- acceptance
- access
- account
- accounting
- accreditation
- accredited
- acronym
- acting
- active
- activities
- adaptation
- address
- addressing
- administration
- admission
- admissions
- adulta
- adults
- advantage
- advantages
- adverb
- adversity
- affairs
- affect
- africa
- after
- agencies
- agency
- agent
- agents
- airforce
- alarm
- alexander
- algebra
- allowed
- alpha
- alphabet
- amber
- america
- american
- americans
- analysis
- analyze
- anatomy
- ancient
- anglo
- animal
- anthropology
- anyone
- anything
- apartment
- apostles
- appalachian
- applicants
- application
- applied
- apply
- applying
- aptitude
- arabic
- architects
- area
- argument
- argumentative
- aristotle
- army
- arrive
- arrows
- article
- artifact
- artifacts
- artistry
- arts
- aruba
- assessment
- assessments
- assimilation
- assistant
- associate
- associates
- asterix
- asvab
- athletic
- attacked
- attend
- attention
- attila
- autobiographical
- autobiography
- average
- aztec
- bachelor
- bachelors
- back
- bags
- bald
- balls
- bank
- banking
- based
- beads
- beautiful
- because
- become
- becoming
- beginner
- beginners
- behavior
- behaviorism
- behaviors
- being
- beliefs
- bella
- below
- benchmark
- benefits
- best
- better
- between
- bible
- biochemistry
- biologists
- biology
- black
- blackbeard
- blend
- blends
- bloom
- boarding
- boats
- book
- boys
- brain
- breaker
- breakers
- breaking
- breaks
- broadcasting
- broker
- bronx
- bulb
- burlap
- business
- bypass
- caddos
- calculate
- calculating
- calculator
- calculus
- call
- called
- cameras
- campaign
- campbell
- canada
- candle
- candles
- capitalize
- card
- cardinal
- cardiologist
- cards
- care
- career
- caribbean
- catapult
- catapults
- catcher
- categorical
- cbest
- center
- central
- ceremony
- certificate
- certification
- challenges
- change
- changes
- changing
- character
- characteristics
- characters
- charlotte
- cheat
- check
- cheerleaders
- cheerleading
- chemical
- chemistry
- cherokee
- child
- choctaw
- choices
- choose
- chose
- christ
- christmas
- churches
- ciao
- city
- civilization
- claims
- class
- classes
- classroom
- clause
- clean
- cleanse
- closing
- clothes
- clothing
- coaches
- coalinga
- coast
- cogat
- college
- colleges
- colonies
- colony
- color
- colors
- comma
- commercial
- common
- communication
- communicator
- community
- competent
- completed
- components
- comprehension
- computer
- concept
- conclude
- concluding
- conclusion
- conclusions
- concrete
- conflicts
- conjugation
- cons
- consonant
- constructivism
- constructivist
- content
- contextual
- contract
- contrast
- contributions
- convert
- cooked
- cooking
- cool
- copy
- core
- cosmetology
- cost
- could
- council
- count
- countries
- course
- courses
- cover
- create
- created
- creating
- creative
- credibility
- credits
- criminal
- criterion
- critical
- critique
- cross
- cultural
- culture
- cultures
- cuny
- currency
- currently
- curriculum
- cursive
- curve
- curves
- custom
- customs
- cute
- cutting
- cypress
- dabate
- dallas
- damaging
- dance
- dangling
- data
- date
- dates
- deactivate
- deans
- debates
- decisions
- declaration
- decline
- decoding
- defensive
- definition
- definitions
- degree
- degrees
- delta
- democrats
- denny
- dependent
- dependents
- dermatologist
- descriptive
- deserve
- design
- designing
- development
- device
- devices
- diagnostic
- dialogue
- dialysis
- dibels
- diction
- difference
- differences
- different
- diploma
- directional
- director
- disabled
- disadvantages
- disciples
- discuss
- discussion
- divison
- doctor
- doctorate
- does
- donate
- donation
- donna
- dont
- dorm
- dorms
- double
- download
- dramatic
- draw
- drawing
- dream
- drop
- dual
- eagle
- earn
- easiest
- ecological
- ecology
- education
- effect
- egypt
- egyptian
- egyptians
- election
- elections
- electrical
- elementary
- elizabethan
- elongate
- emergency
- emory
- employees
- encoding
- ending
- engine
- engineer
- engineerig
- engineering
- england
- english
- enhanced
- entrance
- envelope
- enviorment
- environmental
- erase
- essay
- essays
- estate
- ethical
- ethics
- european
- evaluate
- events
- exactly
- exam
- example
- examples
- excel
- except
- expelled
- expenses
- experiment
- expository
- expulsion
- facs
- fact
- facts
- fafsa
- fail
- failed
- fair
- fake
- fall
- family
- farm
- fashion
- fasion
- faster
- features
- federal
- feudalism
- field
- files
- fill
- film
- final
- financial
- find
- fine
- finish
- finishing
- fire
- firenze
- first
- flag
- flakes
- flashlight
- fleur
- florida
- food
- foods
- football
- foreign
- forensic
- format
- forms
- foster
- founded
- four
- fourth
- framework
- free
- french
- freshman
- freshmen
- friendly
- friends
- from
- full
- function
- fund
- funded
- funny
- gaelic
- game
- games
- geds
- general
- genghis
- genres
- geography
- georgia
- german
- germany
- gesell
- getting
- give
- glasses
- globalization
- glue
- gmail
- goals
- gold
- good
- goodbye
- goodnight
- government
- gown
- gpas
- grabbers
- grade
- graders
- grades
- grading
- graduate
- graduates
- graduating
- graduation
- grammar
- grandchildren
- grant
- grants
- greece
- greek
- group
- growth
- guide
- guides
- guitar
- gulf
- gunsmithing
- gwam
- hair
- hand
- handed
- hands
- happens
- happy
- hard
- harvard
- have
- having
- hbcu
- head
- heading
- hebrew
- hellen
- hellenistic
- hello
- hemodialysis
- high
- higher
- highschool
- hills
- historically
- history
- hobbes
- home
- homecoming
- homes
- homeschool
- honor
- honorary
- honors
- hopkins
- hospital
- hospitality
- hours
- house
- housing
- however
- human
- humane
- humanitoes
- humans
- hvac
- icebreaker
- icebreakers
- idea
- idealism
- ideals
- ideas
- identify
- identifying
- immigrants
- impact
- impacts
- impeach
- imperialism
- importance
- important
- improve
- inaugural
- included
- income
- independence
- india
- indian
- indoor
- induction
- industrial
- influence
- Information
- initiation
- instead
- institute
- interactive
- interesting
- intergrated
- internship
- interpersonal
- intership
- interview
- into
- introduction
- introductions
- invented
- invention
- inventions
- invitation
- involve
- iranians
- ireland
- irish
- iroquois
- italian
- items
- jeffersonian
- jeopardy
- jersey
- jesuit
- jesus
- jobs
- join
- joining
- junior
- juniors
- justice
- kaplan
- kappa
- katana
- kaufman
- keller
- khan
- kids
- kill
- kind
- kindergarten
- know
- known
- labor
- lady
- language
- languages
- large
- last
- late
- latin
- lawyer
- league
- learn
- learned
- learning
- length
- lesson
- lessons
- letter
- letters
- level
- levels
- liberal
- license
- licensed
- life
- lifestyle
- light
- like
- limit
- list
- listening
- lists
- literacy
- literal
- literature
- little
- living
- loan
- loans
- local
- locker
- login
- long
- longer
- longitude
- look
- lords
- love
- luck
- macroeconomic
- made
- main
- mainstreaming
- major
- majors
- make
- makes
- making
- males
- manage
- management
- many
- marine
- marketing
- mascot
- maslow
- maslows
- master
- masters
- mates
- math
- matter
- mayor
- mcat
- mean
- meaning
- means
- media
- medical
- medicine
- medium
- memorize
- memory
- meps
- mesopotamian
- methods
- mexico
- middle
- migrant
- military
- mini
- minimum
- minor
- minute
- miss
- mitchell
- mnemonic
- mockingbird
- modeling
- models
- modern
- modernism
- modernist
- money
- monitor
- monitoring
- morning
- mortar
- most
- movie
- moving
- much
- multicultural
- multiple
- music
- musical
- name
- names
- national
- native
- nature
- navy
- nclex
- near
- need
- needed
- needs
- negative
- negro
- nelson
- neonatal
- netflix
- newspaper
- nkjv
- nominative
- norm
- nostalgic
- notification
- noun
- nouns
- nova
- number
- numbered
- nurse
- nurses
- nursing
- nusing
- obgyn
- object
- objective
- objects
- obtain
- occupational
- oceanographer
- offer
- ohio
- oneself
- online
- open
- opening
- operations
- optometry
- order
- outfitters
- outline
- overall
- overcoming
- overthrow
- pacer
- page
- paper
- papers
- paragraph
- part
- partial
- participle
- parts
- pass
- passing
- passive
- patients
- patterns
- paul
- pell
- penn
- people
- percent
- percentages
- percentile
- performance
- performing
- period
- persian
- personal
- perspective
- persuasive
- pharmacology
- pharmacy
- phoenix
- phonics
- photochemical
- photographic
- photography
- photos
- phrase
- physical
- physician
- physiology
- pictures
- pilot
- placement
- plan
- plant
- plasma
- plastic
- plato
- play
- plays
- pledge
- pledging
- plot
- plural
- poem
- poetry
- point
- pointillism
- pole
- polish
- popcorn
- popular
- population
- portfolio
- positive
- possessive
- post
- postcard
- practice
- predicate
- predicated
- preoperational
- prep
- prepare
- prepositional
- preschool
- preschoolers
- prescriptive
- presentation
- press
- pressure
- preterite
- prima
- primary
- printable
- printing
- priority
- private
- probability
- production
- products
- professor
- program
- programs
- progress
- project
- projects
- prom
- pronoun
- pronounce
- pronouns
- proofreading
- proportion
- pros
- protective
- psychology
- public
- puerto
- purpose
- puzzle
- quantitative
- quarter
- question
- questions
- quickly
- quintile
- quoting
- radiologist
- radiology
- raise
- raising
- range
- ratio
- reached
- reading
- realism
- reasons
- rebus
- recognition
- recognize
- recommendation
- referenced
- reflection
- reflective
- reflexive
- refuge
- regents
- regional
- regions
- register
- reinforcement
- reinforcer
- release
- reliability
- relic
- religion
- remember
- remove
- removing
- rent
- repair
- repay
- repeating
- replace
- report
- reports
- require
- required
- requirement
- requirements
- research
- residents
- respected
- respiratory
- results
- resume
- retake
- reunion
- reunions
- review
- revolution
- rhetorical
- rhit
- rica
- ride
- rituals
- rock
- role
- roles
- room
- root
- rotc
- rubric
- rules
- rush
- salaries
- sale
- same
- sample
- samples
- samurai
- sang
- sanskrit
- satire
- saxon
- scantron
- scared
- scene
- schol
- scholarship
- scholarships
- school
- schooling
- schools
- science
- score
- scores
- scoring
- scotland
- scottish
- seals
- second
- secondary
- section
- sectional
- security
- self
- sell
- sells
- send
- senior
- seniors
- sentence
- sequence
- sequential
- service
- setting
- setup
- sewn
- sheet
- shoe
- short
- should
- show
- siblings
- side
- sight
- sigma
- sign
- simple
- simularitys
- sized
- skill
- skills
- skip
- sleeves
- small
- smog
- social
- society
- software
- some
- someone
- someones
- song
- songs
- sorority
- sound
- sounds
- soup
- source
- spaces
- spanish
- speak
- speaker
- speakers
- speaking
- speech
- speeches
- spell
- spirit
- spoken
- sports
- square
- stages
- stamped
- stand
- standardized
- stanford
- start
- state
- statement
- statements
- states
- statistics
- stay
- steps
- sticks
- stna
- stoles
- stone
- stop
- stopped
- stories
- strategies
- strengths
- structures
- student
- students
- studies
- study
- style
- styles
- subject
- submit
- suffixes
- suite
- summarize
- summarizing
- summary
- summer
- sung
- surgeon
- survival
- suspended
- suspension
- swedish
- syllables
- symbol
- system
- systems
- table
- tables
- take
- talent
- talk
- tampa
- tassel
- tassels
- tbas
- teach
- teacher
- teachers
- teaching
- team
- teams
- technical
- technician
- technology
- teepee
- template
- tenses
- terminology
- terra
- test
- testing
- tests
- texas
- than
- thank
- that
- their
- theme
- themes
- theoretical
- theory
- there
- thesis
- things
- thought
- three
- tier
- tiers
- timberline
- time
- times
- tips
- title
- titles
- toastmasters
- today
- tone
- topics
- toys
- traditional
- training
- transcript
- transfer
- transferring
- transition
- translate
- translated
- treasurer
- trebuchet
- trenton
- trial
- tribes
- tribute
- trip
- tuition
- turning
- tutor
- tying
- type
- types
- typing
- ucla
- under
- undergraduate
- uniforms
- union
- united
- units
- universities
- university
- used
- using
- valedictorian
- validate
- validity
- value
- values
- variables
- varsity
- vassar
- verb
- verbal
- verbs
- verizon
- veteran
- veterinarian
- video
- videos
- view
- views
- viking
- villanova
- virginia
- voice
- volleyball
- vowel
- want
- warrant
- washington
- watch
- ways
- weaknesses
- weapons
- wear
- wearers
- weather
- weighted
- welfare
- were
- wesleyan
- west
- what
- whats
- wheel
- when
- where
- which
- while
- white
- whom
- widow
- wigs
- will
- window
- windows
- with
- without
- women
- wonderlic
- word
- words
- work
- workers
- works
- world
- worry
- worship
- worth
- write
- writing
- xenia
- xray
- year
- yearbooks
- years
- yellow
- york
- young
- your
